The Council for Higher Education Accreditation (CHEA) offers the following statement on the nature of accreditation:
“Accreditation in higher education is defined as a collegial process based on self- and peer assessment for public accountability and improvement of academic quality. Peers assess the quality of an institution or academic program and assist the faculty and staff in improvement.
An accreditation of an academic program or an entire institution typically involves three major activities:”
The Process
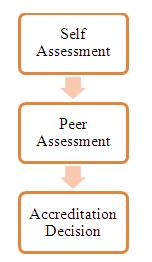
Activity 1
Self Assessment
“The faculty, administrators, and staff of the institution or academic program conduct a self-study using the accrediting organizations set of expectations about quality (standards, criteria) as their guide.”
Activity 2
Peer Assessment
“A team of peers, selected by the accrediting organization, reviews the evidence, visits the campus to interview the faculty and staff, and writes a report of its assessment including recommendation to the commission of the accrediting organization (group of peer faculty and staff, professionals, and public members).”
Activity 3
Accreditation decision
“Guided by a set of expectations about quality and integrity, the commission reviews the evidence and recommendation, makes a judgment, and communicates the decision to the institution and other constituencies if appropriate.”